Understand OKD OpenShift 4 Buildconfig Configurations

In this Post I will show you how you can install rad hat openshift pipelines (Tekton) on OpenShift4.
Parts of the Openshift 4 series
- Part1a: Install Opeshift 4
- Part1b: Install Opeshift 4 with calico
- Part1c: Install Opeshift 4 with cilium
- Part2: Configure OKD OpenShift 4 ingress
- Part3: Configure OKD OpenShift 4 authentication
- Part4: Configure OKD OpenShift 4 Ceph Persisten Storage
- Part5: Configuringure OKD OpenShift 4 registry for bare metal
- Part6a: Install Cluster Logging Operator on OpenShift 4
- Part6b: Openshift: Log4Shell - Remote Code Execution (CVE-2021-44228) (CVE-2021-4104)
- Part7: Understand OKD OpenShift 4 Buildconfig Configurations
- Part8: Install RadHat OpenShift pipelines (Tekton) OKD 4
What is Buildconfig?
Openshift has introduced a new resource called BuildConfig, to support Build Config Openshift developed a new technology called Source-to-Image (S2I) to build pods. S2I provides Openshift capabilities equivalent to Jenkins.
Understand Buildconfig definition
In a Buildconfig definition, there a list of directives to be fill. A sample Buildconfig definition looks like below:
apiVersion: build.openshift.io/v1
kind: BuildConfig
metadata:
name: maven-webapp-build
spec:
runPolicy: <... list the run policy ...>
triggers:
<... list of triggers ...>
source:
<... input parameters or source ...>
strategy:
<... build strategy to use ...>
output:
<... repository details ...>
postCommit:
<... optinal build hooks ...>
Under the spec section source, strategy and output must be filled in order to run the build config.
triggers- Webhooks like GitHub/GitLab webhooks can be used to trigger this build.source- Here you can define the source code repository.strategy- This can beDocker Build,Source-to-ImageorCustom Buildoutput- This directive is used to set an image output repository. This can be either Openshift build in a repository, on-premise private registry or docker hub.
Source-to-Image (S2I) Build
Red Hat introduced Source-to-Image technology in order to reduce workload from developers and allow them to focus on the code. Openshift provides a list of pre-built language images. Those images are built with S2I binary, all the essential libraries, and tools needed for the development environment.
Openshift ImageStream Configuration Example
First we ned to create an ImageStream to store the image. This is a folder in OKD’s local dcker registry.
nano ImageStream.yaml
---
apiVersion: image.openshift.io/v1
kind: ImageStream
metadata:
name: maven-webapp
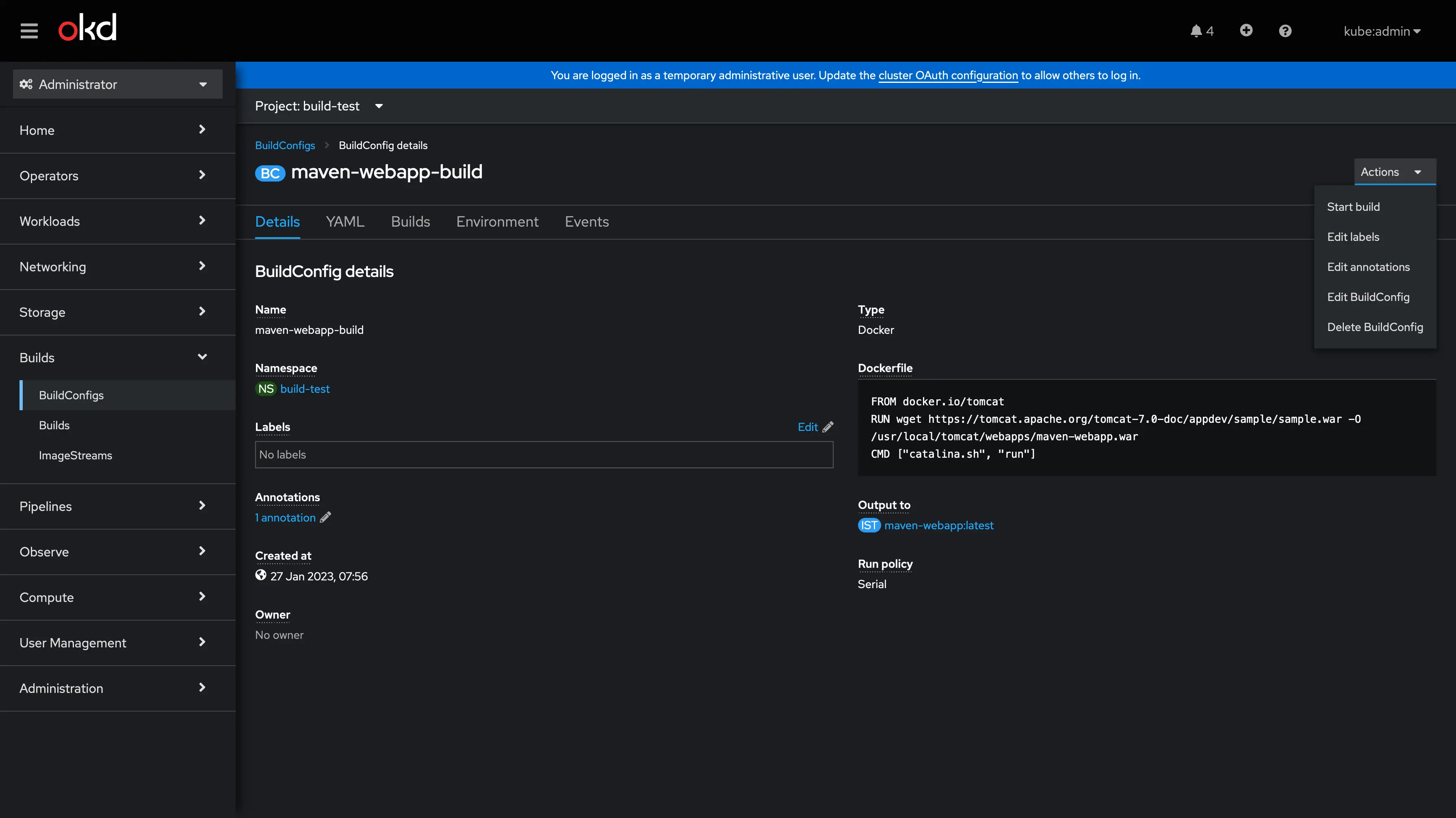
Openshift BuildConfig Configuration Example - 1
nano BuildConfig.yaml
---
apiVersion: build.openshift.io/v1
kind: BuildConfig
metadata:
name: maven-webapp-build
spec:
source:
type: Dockerfile
dockerfile: |
FROM docker.io/tomcat
RUN wget https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-7.0-doc/appdev/sample/sample.war -O /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/maven-webapp.war
CMD ["catalina.sh", "run"]
strategy:
type: Docker
output:
to:
kind: ImageStreamTag
name: 'maven-webapp:latest'
I this BuildConfig I created a Docker build this is the name of the strategy too. For Docker build the source is a Dockerfile. As you can see the content of the Dockerfile is directly in the object. In the end the output is an ImageStream.
Openshift BuildConfig Configuration Example - 2
In this example, I will explain how to use Docker Build Strategy and Git repositories. In this, I hosted all resources on the Github repository.
nano BuildConfig2.yaml
---
apiVersion: build.openshift.io/v1
kind: BuildConfig
metadata:
name: maven-webapp-build2
spec:
source:
type: Git
git:
uri: 'https://github.com/devopstales/maven-web-project.git'
ref: main
contextDir: sample
strategy:
type: Docker
#With this you can set a path to the docker file
#dockerStrategy:
# dockerfilePath: dockerfile
output:
to:
kind: ImageStreamTag
name: 'maven-webapp:latest'
Openshift BuildConfig Configuration Example - 3
In this example, I am using the source strategy for Source-to-Image (S2I) Build:
nano BuildConfig3.yaml
---
kind: BuildConfig
apiVersion: build.openshift.io/v1
metadata:
name: centos-s2i
namespace: build-test
spec:
output:
to:
kind: ImageStreamTag
name: 'maven-webapp:latest'
strategy:
type: Docker
dockerStrategy:
dockerfilePath: Dockerfile
source:
type: Git
git:
uri: 'https://github.com/devopstales/maven-web-project'
ref: main
contextDir: /S2I
The build pods
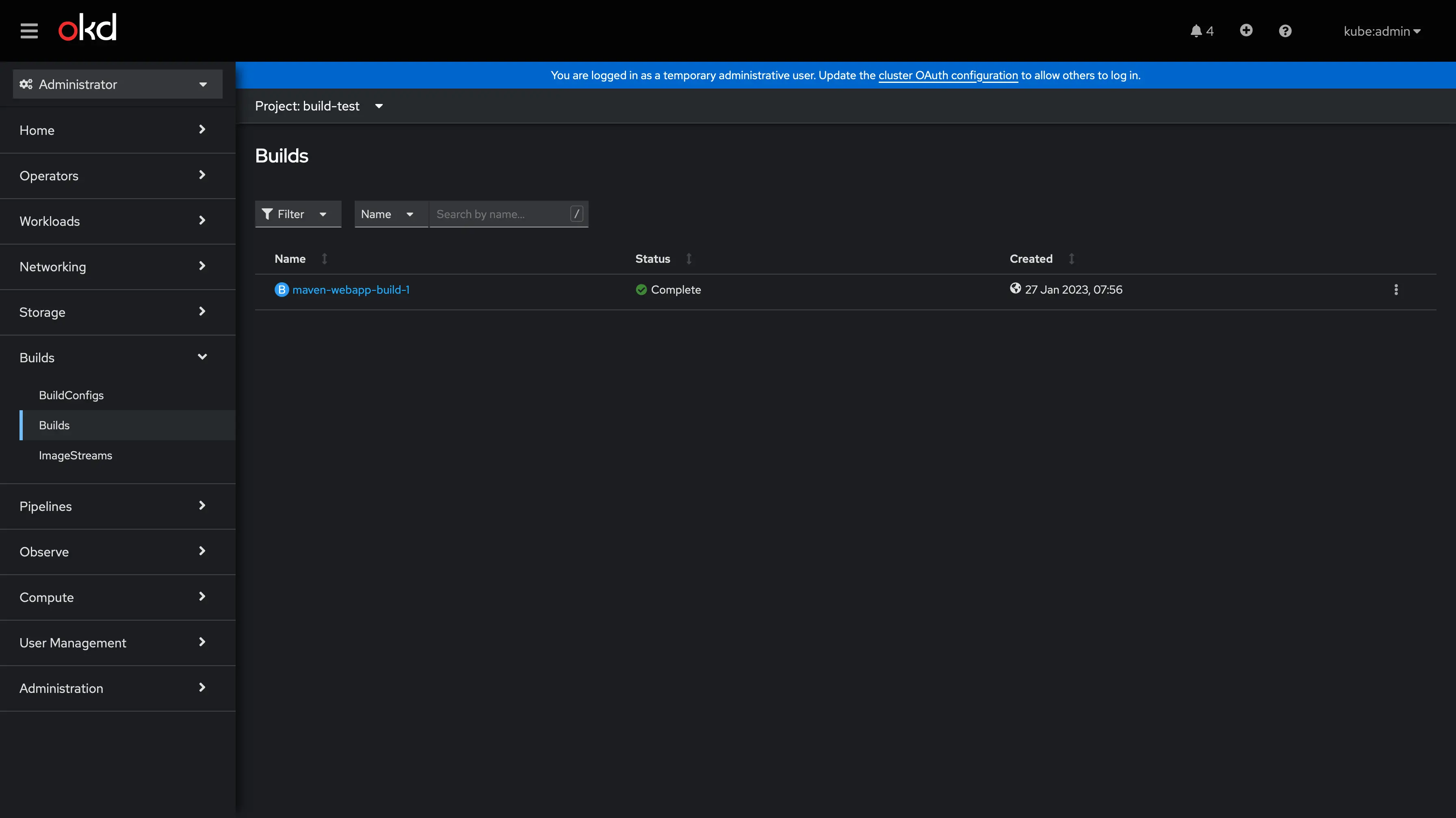
Openshift Use pods to uild the images so if a bild is unsuccessfull the build pod stuck in Error status:
kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
maven-webapp-build-1-build 0/1 Error 0 66m
maven-webapp-build-2-build 0/1 Error 0 44m
maven-webapp-build-3-build 0/1 Error 0 42m
maven-webapp-build-4-build 0/1 Completed 0 39m
maven-webapp-build2-1-build 0/1 Init:Error 0 31m
maven-webapp-build2-2-build 0/1 Error 0 28m
maven-webapp-build2-3-build 0/1 Init:Error 0 5m50s
maven-webapp-build2-4-build 0/1 Completed 0 5m14s
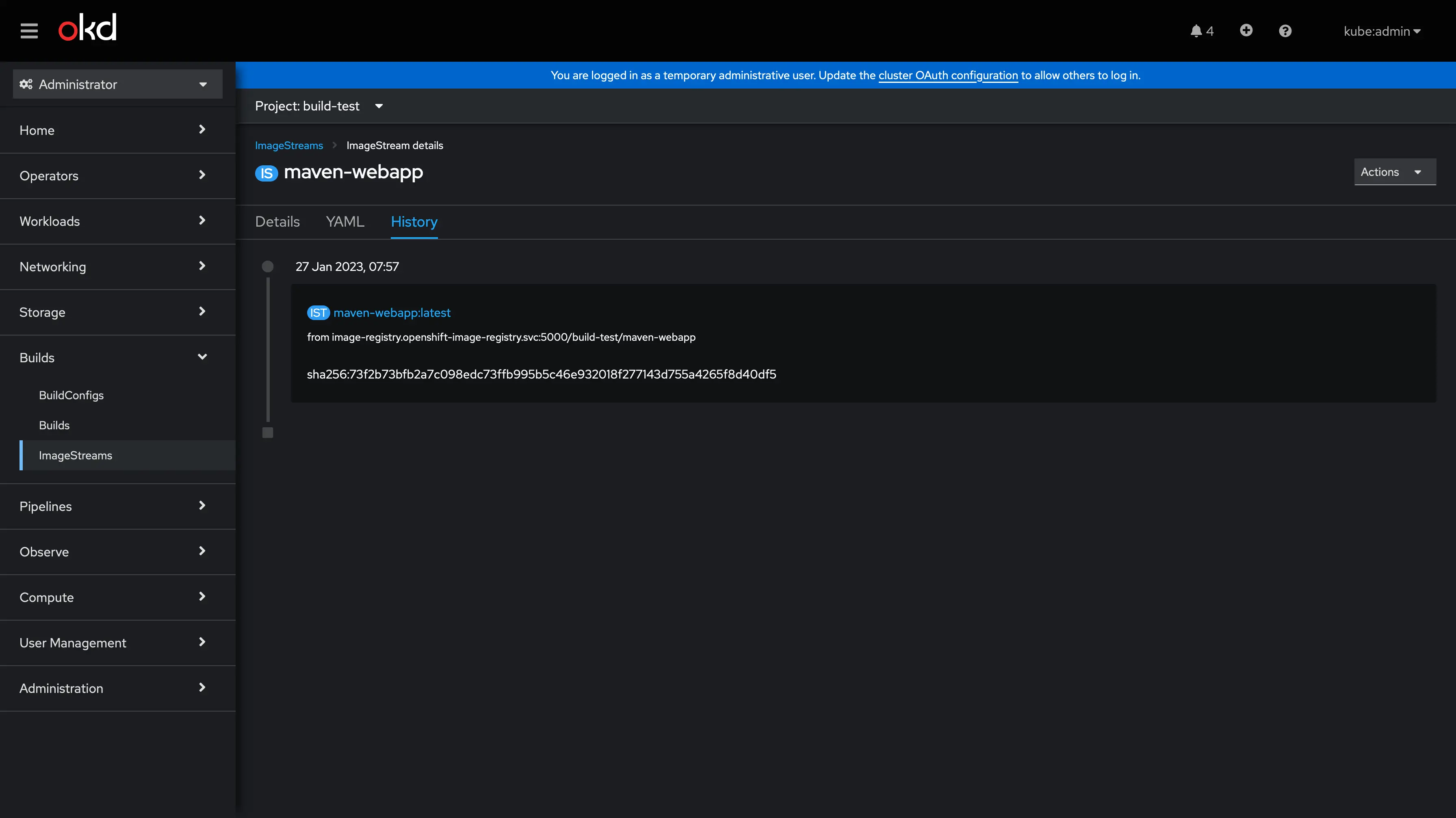
How tu use the ImageStream to Automatcle update image in Deployment?
You can define an ImageStream in the DeploymentConfig object to trigger image update:
nano DeploymentConfig.yaml
---
apiVersion: apps.openshift.io/v1
kind: DeploymentConfig
metadata:
name: maven-webapp
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
app: maven-webapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: maven-webapp
spec:
containers:
- name: maven-webapp
image: ''
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
triggers:
- type: ConfigChange
- type: ImageChange
imageChangeParams:
automatic: true
containerNames:
- maven-webapp
from:
kind: ImageStreamTag
name: maven-webapp:latest
Set up a GitHub webhook
Add GitHub type trigger for your BuildConfig.
nano BuildConfig3.yaml
---
kind: BuildConfig
apiVersion: build.openshift.io/v1
metadata:
name: centos-s2i
namespace: build-test
spec:
output:
to:
kind: ImageStreamTag
name: 'maven-webapp:latest'
strategy:
type: Docker
dockerStrategy:
dockerfilePath: Dockerfile
source:
type: Git
git:
uri: 'https://github.com/devopstales/maven-web-project'
ref: main
contextDir: /S2I
triggers:
- type: Generic
generic:
secretReference:
name: centos-s2i-generic-webhook-secret
- type: GitHub
github:
secretReference:
name: centos-s2i-github-webhook-secret
- type: ConfigChange
GitHub webhooks allow external services to be notified when certain events happen. To automatically deploy a new pod when updates to the GitHub Dockerfile occur, you must configure your GitHub repo with the webhook that OpenShift provides as part of the BuildConfig.
- In the
DevelopmentUI go toBuilds, select yourBuildConfig - Go to the Webhooks section and click Copy URL with Secret for the Generic webhook type.
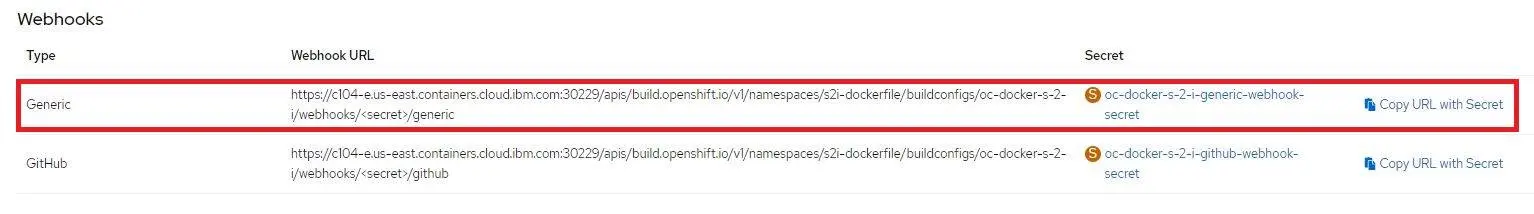
- Open your GitHub repo and navigate to
Settings. - Select
Webhooksfrom the Options menu and clickAdd Webhook.
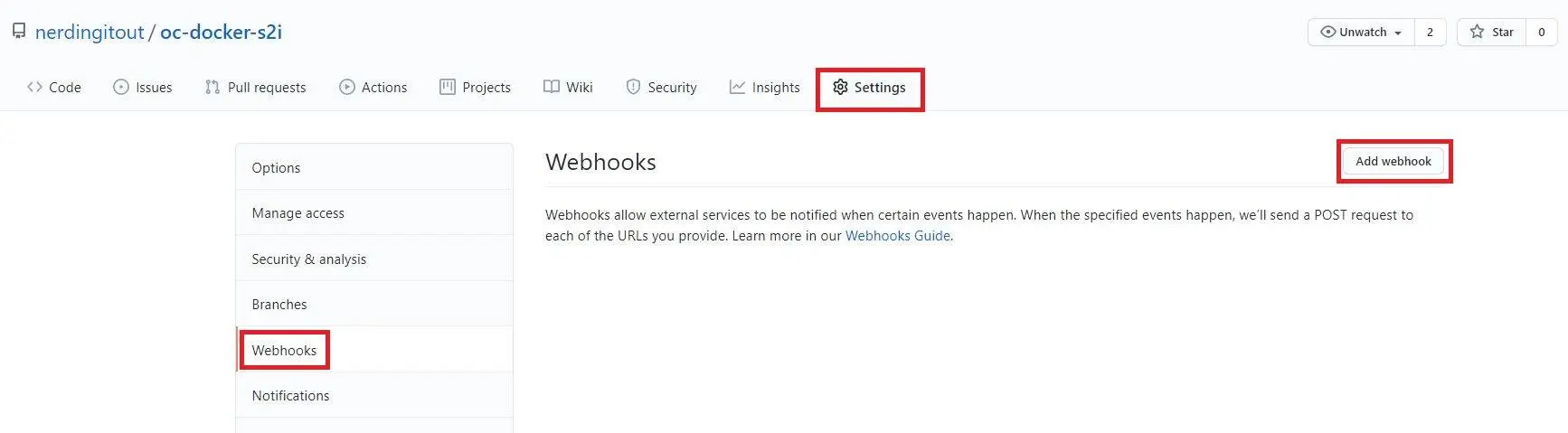
- On the
Add webhookpage, paste the URL that you copied earlier into thePayload URLfield. - In the
Content typefield, select theapplication/jsonoption. - Click
Add webhook.
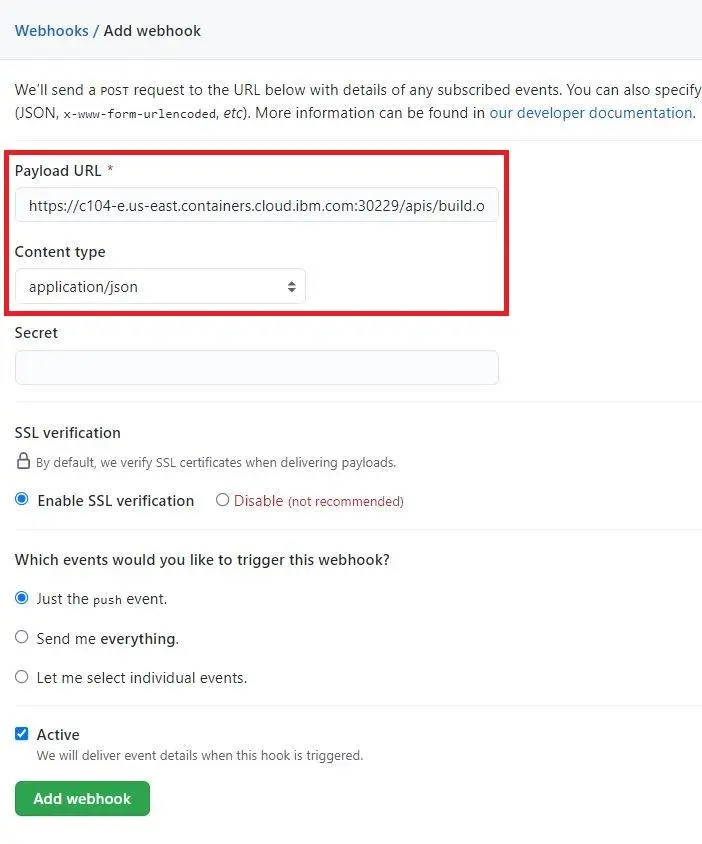
Select your newly added webhook to see its details. The Recent Deliveries section displays an entry for a ping test that is prefixed with a tick mark, which indicates that the ping test was successful.
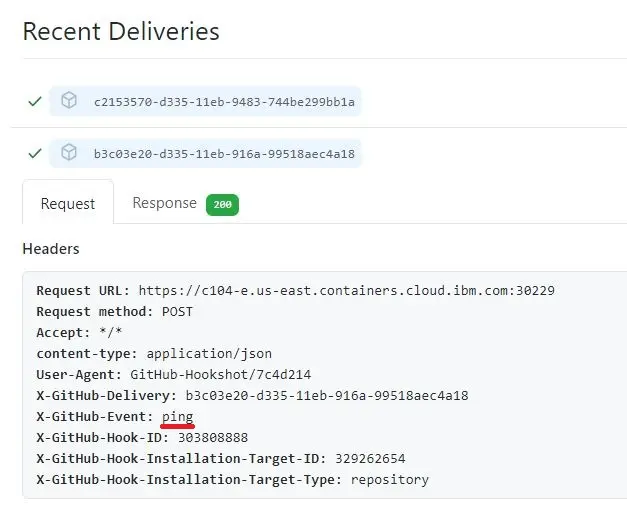
Click the entry to view more details about the REST API call and the associated response for the ping test. A successful ping test indicates that GitHub is able to connect with your OpenShift cluster.

