Image Signature Verification with Kyverno
In this post I will show you how you can use Kyverno and Cosign for Image Signature Verification in a Kubernetes cluster.
Parts of the K8S Security Lab series
Container Runetime Security
- Part1: How to deploy CRI-O with Firecracker?
- Part2: How to deploy CRI-O with gVisor?
- Part3: How to deploy containerd with Firecracker?
- Part4: How to deploy containerd with gVisor?
- Part5: How to deploy containerd with kata containers?
Advanced Kernel Security
- Part1: Hardening Kubernetes with seccomp
- Part2: Linux user namespace management wit CRI-O in Kubernetes
- Part3: Hardening Kubernetes with seccomp
Network Security
- Part1: RKE2 Install With Calico
- Part2: RKE2 Install With Cilium
- Part3: CNI-Genie: network separation with multiple CNI
- Part3: Configurre network wit nmstate operator
- Part3: Kubernetes Network Policy
- Part4: Kubernetes with external Ingress Controller with vxlan
- Part4: Kubernetes with external Ingress Controller with bgp
- Part4: Central authentication with oauth2-proxy
- Part5: Secure your applications with Pomerium Ingress Controller
- Part6: CrowdSec Intrusion Detection System (IDS) for Kubernetes
- Part7: Kubernetes audit logs and Falco
Secure Kubernetes Install
- Part1: Best Practices to keeping Kubernetes Clusters Secure
- Part2: Kubernetes Secure Install
- Part3: Kubernetes Hardening Guide with CIS 1.6 Benchmark
- Part4: Kubernetes Certificate Rotation
User Security
- Part1: How to create kubeconfig?
- Part2: How to create Users in Kubernetes the right way?
- Part3: Kubernetes Single Sign-on with Pinniped OpenID Connect
- Part4: Kubectl authentication with Kuberos Depricated !!
- Part5: Kubernetes authentication with Keycloak and gangway Depricated !!
- Part6: kube-openid-connect 1.0 Depricated !!
Image Security
Pod Security
- Part1: Using Admission Controllers
- Part2: RKE2 Pod Security Policy
- Part3: Kubernetes Pod Security Admission
- Part4: Kubernetes: How to migrate Pod Security Policy to Pod Security Admission?
- Part5: Pod Security Standards using Kyverno
- Part6: Kubernetes Cluster Policy with Kyverno
Secret Security
- Part1: Kubernetes and Vault integration
- Part2: Kubernetes External Vault integration
- Part3: ArgoCD and kubeseal to encript secrets
- Part4: Flux2 and kubeseal to encrypt secrets
- Part5: Flux2 and Mozilla SOPS to encrypt secrets
Monitoring and Observability
- Part6: K8S Logging And Monitoring
- Part7: Install Grafana Loki with Helm3
Backup
Wat is Cosign?
Cosign is a new open-source tool to manage the process of signing and verifying container images. Developed by Googele in collaboration with Linux Foundation’s sigstore project. The motivation for cosign is “to make signatures invisible infrastructure.” With Images signed by Cosign you didn’t neet to change your infrastructure to store the public signing key, like Notary. (With Notary you need a Notary server connected to your registry to store the keys) With Cosign, the signatures directly appear as tags of the image linked to the associated image via the digest:
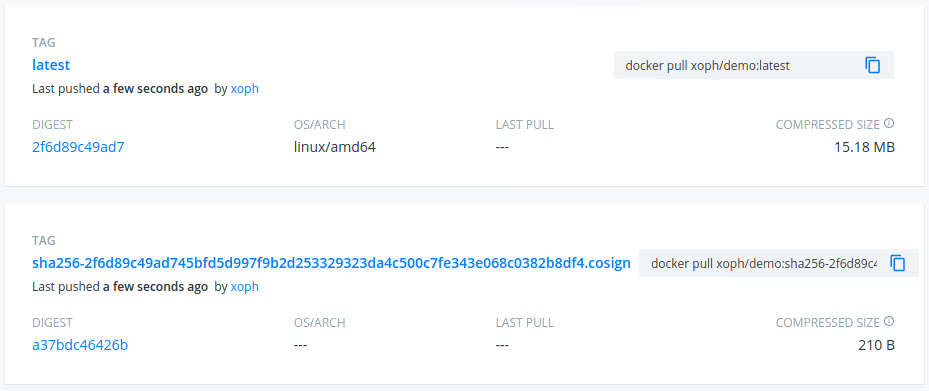
Key Management options:
- fixed, text-based keys generated using
cosign generate-key-pair - cloud KMS-based keys generated using
cosign generate-key-pair -kms - keys generated on hardware tokens using the PIV interface using
cosign piv-tool - Kubernetes-secret based keys generated using
cosign generate-key-pair -k8s
Installing Cosign
It’s a golang project, so it’s fairly easy to get started, there’s a single binary available from their release pag and it has been signed by them.
Generate key pair with:
$ cosign generate-key-pair
Enter password for private key:
Enter again:
Private key written to cosign.key
Public key written to cosign.pub
Sign an image with cosign:
docker pull alpine:edge
docker tag alpine:edge devopstales/testimage:unsigned
docker push devopstales/testimage:unsigned
docker pull alpine:latest
docker tag alpine:latest devopstales/testimage:cosign
docker push devopstales/testimage:cosign
cosign sign -key ~/data/cosign.key devopstales/testimage:cosign
Enter password for private key:
Pushing signature to: index.docker.io/devopstales/testimage:sha256-4661fb57f7890b9145907a1fe2555091d333ff3d28db86c3bb906f6a2be93c87.sig
Verify a container against a public key:
$ cosign verify -key ~/data/cosign.pub devopstales/testimage:cosign
Verification for devopstales/testimage:cosign --
The following checks were performed on each of these signatures:
- The cosign claims were validated
- The signatures were verified against the specified public key
- Any certificates were verified against the Fulcio roots.
{"critical":{"identity":{"docker-reference":"index.docker.io/devopstales/testimage"},"image":{"docker-manifest-digest":"sha256:4661fb57f7890b9145907a1fe2555091d333ff3d28db86c3bb906f6a2be93c87"},"type":"cosign container image signature"},"optional":null}
Image Signature Verification tools
In a previous post I used Connaisseur to Image Signature Verification. I could youse Connaisseur with Cosign too but with the new release of Kyverno we didn’t need to deploy a separate tool for Image Signature Verification. We can use Kyverno’s verifyImages rule.
It validate signatures for matching images using Cosign and mutates image references with the digest returned by Cosign. Using an image digest guarantees immutability of images and hence improves security.
Install the latest version of Kyverno:
kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kyverno/kyverno/main/definitions/release/install.yaml
Patch the Kyverno webhook, to allow time for calling the OCI registry:
kubectl patch mutatingwebhookconfigurations kyverno-resource-mutating-webhook-cfg \
--type json \
-p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/webhooks/0/failurePolicy", "value": "Ignore"},{"op": "replace", "path": "/webhooks/0/timeoutSeconds", "value": 15}]'
Here is a policy that verifies all images from a specific repository:
apiVersion: kyverno.io/v1
kind: ClusterPolicy
metadata:
name: check-image
spec:
validationFailureAction: enforce
background: false
rules:
- name: check-image
match:
resources:
kinds:
- Pod
verifyImages:
- image: "docker.io/devopstales/testimage:*"
key: |-
-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----
MFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAEL53O1V5FP2Vaa60BTwRjrOxhuu5C
iB/mODf/V2eiGw+WbA689ZZRjWwXCf+4jwzfRSrik0YvTCMqvl3BDaPG2A==
-----END PUBLIC KEY-----
kubectl create deployment signed-my \
--image=devopstales/testimage:cosign
Try running an unsigned image that matches the configured rule:
kubectl create deployment unsigned-my \
--image=docker.io/devopstales/testimage:unsigned
This will be blocked:
error: failed to create deployment: admission webhook "mutate.kyverno.svc" denied the request:
resource Deployment/kyverno-system/unsigned-my was blocked due to the following policies
verify-image:
autogen-verify-image: 'image verification failed for docker.io/devopstales/testimage:unsigned:
failed to verify image: fetching signatures: getting signature manifest: GET https://index.docker.io/v2/devopstales/testimage/manifests/sha256-0119f88f395766eb52f9b817c3d23576bf31935dc8e94abe14bae9a083ce4639.sig:
MANIFEST_UNKNOWN: manifest unknown; map[Tag:sha256-0119f88f395766eb52f9b817c3d23576bf31935dc8e94abe14bae9a083ce4639.sig]'

